Absenteeism is a complex challenge that affects not only individual productivity but also the cohesion and performance of entire teams.
Absenteeism occurs when an employee is frequently absent from work — whether justified or unjustified. This behavior can stem from various causes ranging from personal health issues to dissatisfaction with the workplace.
Boost your team’s efficiency with Hubstaff's productivity tools
Try it free for 14 daysIn 2023, absenteeism hit a ten-year high.
The cost of high absenteeism adds up big for businesses, so understanding and preventing employee absences should be a priority for leaders.
In this post, we’ll discuss the reasons behind absenteeism and explore its consequences on team dynamics and organizational success, providing insights into how businesses can address this issue.
What is absenteeism?
Absenteeism is the habitual non-presence of an employee at their job. Chronic absenteeism is when employees skip work repeatedly without a good reason or frequently take unneeded sick days.
An employee’s unexcused absences are deemed habitual when they exceed the allotted paid time off and sick days provided by their employer. Habitual absenteeism is more than a casual workplace issue — it disrupts team unity and dramatically reduces productivity.

According to the CDC, businesses lose $225.8 billion yearly due to productivity losses caused by workforce absences. On top of the financial implications, absenteeism has ripple effects. It also impacts employee morale and overall operational efficiency.
The first step in combatting absenteeism is understanding it.
What are the causes of absenteeism?
Absenteeism in the workplace can stem from a variety of sources and can range from valid, legitimate absences to negligent and harmful no-shows.
For our discussion today, we’ve broadly categorized absenteeism into:
- Health-related absences
- Work-related absences
- Personal absences
- Other absences
Health-related reasons
NIOSH tracks absences reported by full-time employees due to illness, injury, or medical issues — known as health-related workplace absenteeism. In 2023, the absence rate was 3.1%.

(Source)
Health-related absenteeism can occur due to:
- Chronic illnesses: Employee health concerns such as diabetes, heart disease, or arthritis that require ongoing treatment and management can lead to regular absences.
- Acute illnesses: Temporary but severe conditions like flu or infections that make it impossible to work. Over a million people have called out of work sick every month in the United States in the past three years. Experts attribute this higher-than-usual absenteeism to COVID-19.
- Mental health issues: Depression, anxiety, and other psychiatric conditions that can impair an individual’s ability to perform their job functions. Mental-health-related absences contribute to the loss of 12 billion workdays globally.
Work-related reasons
Work-related factors play a significant role in employee attendance. Various issues within the workplace can lead to absenteeism. This affects not only the individual’s well-being but also the overall productivity of the organization.
Work-related issues that can cause employees to avoid work include:
- Job dissatisfaction: A lack of engagement with the job tasks, disagreement with management, or inadequate working conditions can push employees to skip work due to stress. Stress alone causes almost a million employees to miss work every day.
- Lack of employee engagement: This can result from poor company culture, lack of recognition, or insufficient compensation. The cost of disengaged employees is $8.8 trillion every year.
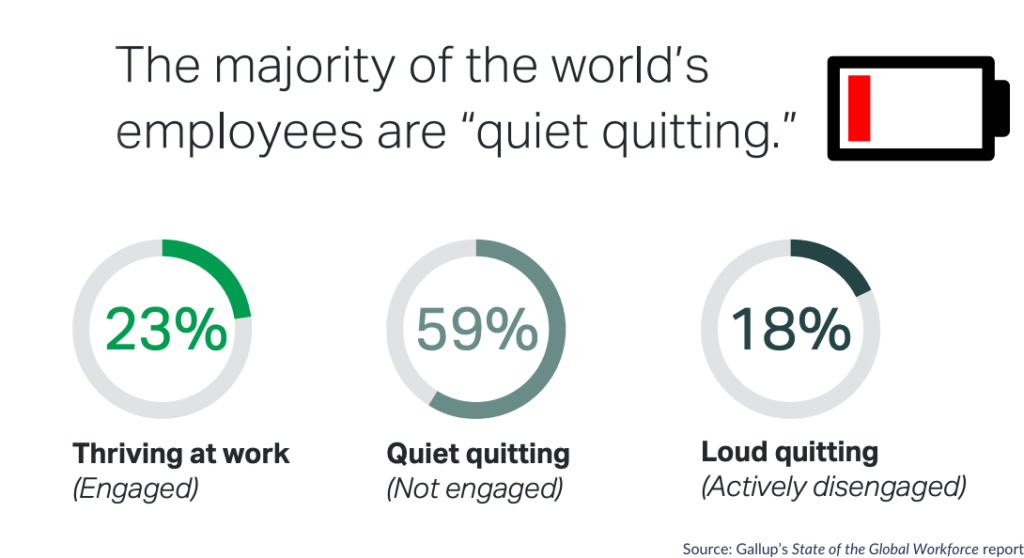
- Employee burnout: Often overlooked, burnout is a state of emotional, physical, and mental exhaustion caused by excessive and prolonged stress at work, leading to absences. A survey found that 76% of participants reported stress as their top reason for taking time off work.
Personal reasons
Nearly 40% of employees miss work due to personal matters. An absent employee may be a cry for help that employers need to respond to and ensure the employee is receiving support.
“Personal reasons” can be chalked up to many different things, but the primary factors we have found are:
- Childcare and eldercare responsibilities: Employees may need to miss work unexpectedly due to issues related to childcare. Whether it’s a sick child or an eldercare emergency with an elderly family member, the lack of reliable backup care or sudden school closures can force parents and caregivers to stay home.
- Mental health days: Increasing awareness and destigmatization of mental health issues have led more employees to recognize that mental health is just as critical as physical health. This then leads employees to take days off for their mental and emotional well-being. While these days are essential for long-term productivity and health, they still contribute to overall absenteeism figures.
Other factors
Some factors that impact absenteeism that don’t fall under the umbrella of personal reasons, work-related concerns, and health-related absence include:
- Educational commitments: Some employees pursue further education to advance their career prospects, which might involve classes, exams, or related commitments during working hours. Although this can lead to short-term absenteeism, the potential for long-term professional growth is worth it.
- Legal and civic obligations: Occasionally, employees need to attend to legal matters such as court appearances, jury duty, or other civic obligations that can’t be scheduled outside of work hours. These mandatory commitments are necessary and justified, but they still contribute to overall absenteeism rates.
By being aware of and addressing these issues, organizations can better understand the root causes behind absenteeism. Before we get into prevention, let’s get on the same page about the stakes for everyone involved.
Consequences of absenteeism
Absenteeism is particularly costly for businesses, but company profits are not the only thing absenteeism can impact.
Absenteeism can have negative consequences for employees and even society as a whole. First, let’s start with the most obvious victim of employee absenteeism: businesses.
For the organization
The indirect costs of absenteeism in the workplace should concern managers and business owners and serve as an encouragement to step in when an employee shows signs of excessive absenteeism in the workplace.
Absenteeism can impact businesses by:
- Reducing productivity: Fewer people to perform necessary tasks can delay or decrease output. The average productivity loss associated with an unplanned employee absence is 22.6%.

- Increasing costs: Employee absenteeism is a significant cost to businesses; covering for absent employees may require overtime pay or temporary staffing. Plus, the CDC estimates that lost productivity from absenteeism costs employers $1,685 per employee each year.
- Lowering morale among other employees: Absenteeism can have a dangerous snowball effect. Increased workload for others can lead to stress and further absenteeism.
For the individual
Absenteeism not only disrupts the daily operations of a workplace but also has profound personal consequences for the individual involved.
Chronic absenteeism can lead to significant impacts on a person’s professional life, including:
- Loss of income: Especially in jobs without paid sick leave, absenteeism can result in direct financial consequences for employees. Each day missed beyond an employee’s PTO or sick leave means a reduction in pay.
- Job insecurity: Chronic absenteeism might lead to disciplinary action or even termination. Consistent absence can be viewed as unreliability or a lack of commitment to the job. Over time, an employee’s perceived dependability and value to the company diminish.
- Poor career prospects: Unscheduled absences can create gaps in performance and achievements, stifling professional growth and advancement. An employee who is frequently absent may miss out on opportunities for projects or promotions, negatively impacting their career trajectory.
To improve the understanding and management of absenteeism, organizations often need to investigate the root causes and develop comprehensive strategies to address them, enhancing employee satisfaction and organizational performance.
For society
Absenteeism’s impact extends beyond individual workplaces, casting a shadow on broader societal structures. It influences various aspects of economic and social life, often leading to cascading effects that can be felt across multiple sectors.
Societal impacts of absenteeism include:
- Increased consumer costs: Businesses often incur additional costs due to absenteeism. These costs negatively impact profitability and lead to higher prices for goods and services.
- Health care costs: Absenteeism related to health issues can lead to increased health care utilization, raising costs for public and private health insurers and impacting the overall health care system’s efficiency.
- Challenges in planning and policy-making: High levels of absenteeism can complicate efforts to plan and implement policies in workplaces and public services. This then makes it more difficult to address broader social and economic challenges.
While absenteeism affects individual workplaces, its broader implications include economic performance, public service delivery, social equality, and health outcomes, making it a significant societal issue.
Fortunately, leaders can develop strategies to mitigate these issues, ultimately fostering a more supportive and productive work environment.
Strategies to reduce absenteeism
The stakes are high, but luckily, businesses can take steps to stop absenteeism in its tracks.
To effectively reduce absenteeism, organizations must adopt a multifaceted approach that addresses the root causes of absences while promoting a positive work environment.
Foster employee engagement
Engaged employees are less likely to miss work unnecessarily as they will feel a stronger connection to their jobs and the organization.
By actively fostering employee engagement, companies can not only enhance overall job satisfaction but also significantly decrease absenteeism rates.

Strategies for implementation
- Give regular feedback
- Build employee recognition programs
- Focus on opportunities for professional growth
- Have regular check-ins with employees
Organizations can decrease absenteeism rates significantly by making employees feel valued and part of a team.
Implement supportive policies
Creating policies that support work-life balance can help reduce absenteeism. This includes flexible working hours, remote work, and adequate paid leave.
Employees who feel that their personal life is respected and can be easily managed alongside their professional responsibilities are more likely to be present and productive at work.
Strategies for implementation
- Ensure holidays, sick leave, and annual leave are generous and up to industry standards
- Enable flexible, remote work
- Enforce the attendance policy fairly
Promote health and wellness
Implementing wellness programs that encourage healthy lifestyles can decrease health-related absences. Healthier employees are generally less prone to illness, which can then reduce absenteeism.
Strategies for implementation
- Include private health insurance and mental health services for employees
- Motivate team members to use their PTO and take time off to reset
- Implement structured wellness challenges and incentives
By integrating these strategies into the workplace, companies can not only enhance the physical and mental well-being of their employees but also create a supportive environment that reduces absenteeism.
Final step: Utilize a time tracking app
Adopting a workforce management tool like Hubstaff can help organizations monitor attendance and productivity efficiently.

How Hubstaff helps prevent absenteeism
- Enhanced monitoring of attendance and productivity: Hubstaff allows managers to track time spent on various tasks and projects, offering insights into how work is done. These insights can help identify any discrepancies or inefficiencies.
- Identification of absenteeism patterns: By analyzing time tracking data, organizations can spot trends in absenteeism, like frequent absences at specific times or days. Understanding these patterns allows management to address potential issues proactively.
- Support for remote and flexible work arrangements: Hubstaff is especially beneficial in managing remote or flexible work arrangements. The app’s ability to track time remotely helps maintain accountability and transparency, ensuring that team members are productive regardless of their physical location.
- Shift scheduling. Hubstaff’s auto-scheduling features make shift scheduling a breeze. Set recurring shifts, turn on alerts, and make real-time adjustments to ensure schedules are correct and reduce absenteeism.
By using a sophisticated workforce management tool like Hubstaff, organizations can create a more structured and data-driven approach to managing employee time. This not only minimizes absenteeism and its associated costs but also contributes significantly to enhancing overall organizational efficiency and success.
Have any other tools or tips for addressing absenteeism? We’d love to hear from you.
Most popular
How to Calculate a Raise: Practical Guide for Employers
By 2030, the US alone will lose $430 billion annually due to low talent retention — and a lot of this turnover stems from low pa...
How to Survive and Thrive in an 80-Hour Work Week
It’s hard to believe that only a century ago, the 80-hour work week was the norm in the United States. Then, in 1926, the Ford M...
Mastering Workforce Scheduling: Techniques and Tools for Success
Imagine a workday where scheduling your workforce effectively ensures that every shift is perfectly aligned with your business nee...
Top Time Trackers for Virtual Assistants: Enhance Efficiency and Accountability
Virtual assistants (VAs) have a lot of responsibilities — and so do the people who hire them. With so much to keep track of, a t...




