If you’re wondering how to figure out labor costs for your business, you’re not alone. Navigating that labyrinth can be daunting for businesses of all sizes and industries. However, understanding and effectively managing these costs is crucial for the overall financial health of your business.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of labor cost calculation, explore the factors influencing these costs, and also equip you with practical tips to streamline labor cost management. Let’s get started.
Boost your team’s efficiency with Hubstaff's productivity tools
Try it free for 14 daysIntroduction to labor costs
Labor costs often represent a substantial portion of a business’s budget. Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, managing these costs efficiently can significantly impact your bottom line.
Definition and importance of labor cost calculation
Labor cost calculation involves taking the sum of all expenses related to employing your workforce. These expenses include all wages and salaries, as well as additional expenditures like benefits, taxes, and other overhead costs.
Accurate labor cost calculations are essential for several reasons:
- Profitability. By understanding your employee costs, you can make informed decisions about pricing, production levels, and staffing. This can then help ensure that your business becomes more profitable.
- Budgeting. Precise labor cost calculation allows for effective budgeting and financial forecasting. The better you budget, the easier it will be to allocate resources efficiently and anticipate potential challenges.
- Compliance. Staying compliant with labor laws and regulations requires accurate labor cost tracking and reporting.
- Performance evaluation. Evaluating labor costs against productivity and revenue can reveal insights into your workforce’s efficiency and help you identify areas for improvement.
Factors affecting labor costs
Several factors can influence your business’ labor costs.
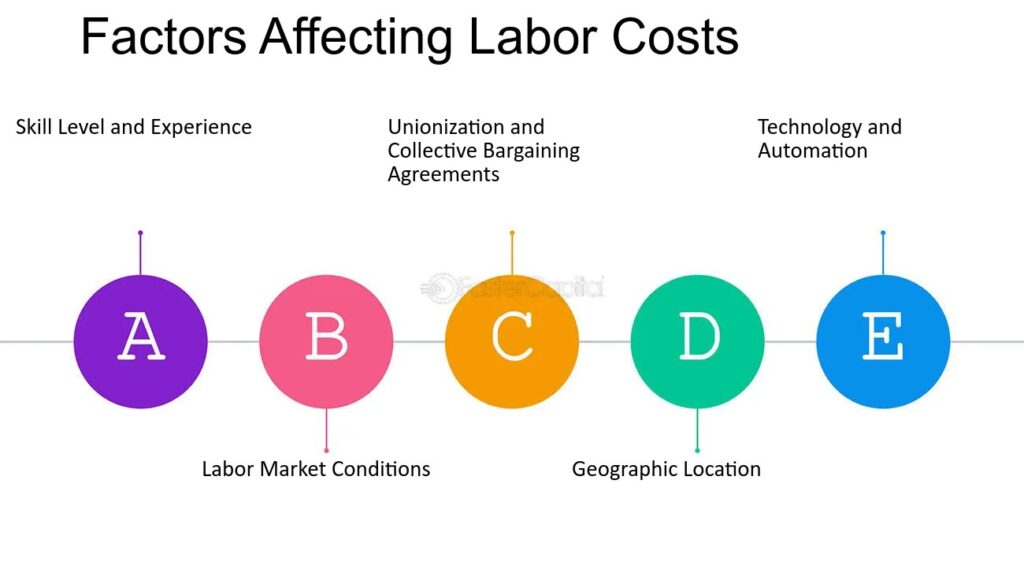
(Source: Faster Capital)
Understanding these factors is vital to effective cost management:
- Employee experience and skills. Highly skilled and experienced employees typically command higher salaries and wages. They also tend to advance within the company, leading to pay raises and promotions.
- Labor market conditions and regulations. Payroll taxes, unemployment insurance, and workers’ compensation insurance are mandatory expenses contributing to labor costs.
- Unionization benefits and perks. Employee benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off are a substantial component of employee costs.
- Use of technology. Businesses that leverage technological solutions typically report lower labor costs. Time tracking and workforce analytics tools help you identify whether or not employees are working, what apps make them most and least productive, and more.
- Industry and location. Labor costs can vary significantly depending on your industry and geographic location. For example, registering an LLC in Florida can be advantageous due to its relatively low labor costs compared to other states. By considering labor costs during the initial registration, you can make a more informed decision and ensure better financial stability for your business.
The basic formula for calculating labor costs
Labor cost calculations may seem complex, but the basic labor cost formula is relatively straightforward. So, how’s labor cost calculated? Let’s take a look.
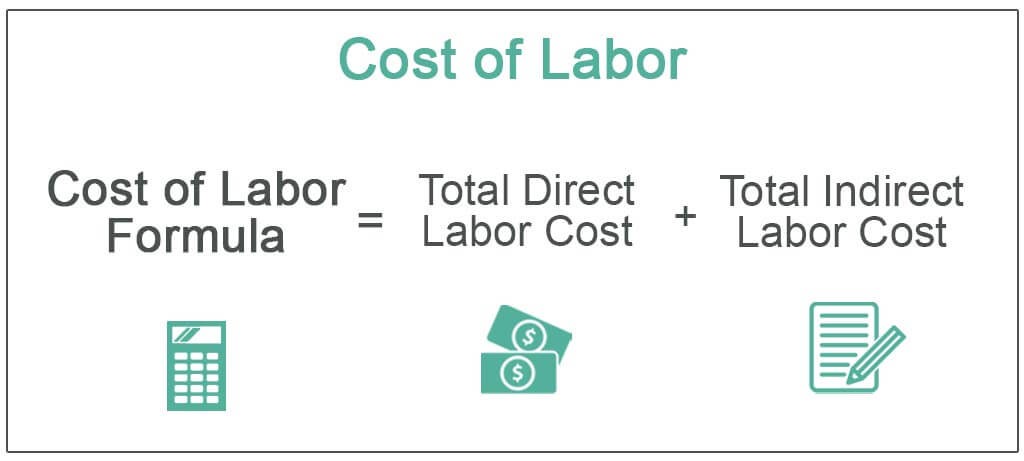
(Source: Wall Street Mojo)
Here’s the formula:
Total Labor Costs = Total Direct Labor Cost + Total Indirect Labor Cost
Components of direct labor costs
The direct labor cost formula adds the components of direct labor. Depending on your payment structure, direct labor costs may include:
- Wages and salaries of employees directly linked to the production of goods or services
- Additional costs directly linked to the production of goods or services
- Commissions and bonuses
Components of indirect labor costs
Indirect labor costs encompass expenses not directly tied to production, like:
- The wages and salaries of employees are not directly linked to production (usually admins, office staff, maintenance crews, etc.).
- Employee benefits
- Recruitment costs
- Training costs
- Payroll taxes
It’s important to note that a critical first step in calculating labor costs is accurately classifying employees as exempt or non-exempt. Exempt vs. non-exempt employees are subject to different wage and hour regulations. These stipulations can then impact overtime pay, minimum wage requirements, and recordkeeping obligations.
For example, employers must pay non-exempt employees overtime for hours worked beyond the standard workweek. Conversely, employers pay exempt employees a fixed salary regardless of the hours they work.
Calculating labor cost per hour and per day
Labor costs calculated on an hourly or daily basis can help you gain a deeper understanding of your finances and efficiency. Let’s look at the formulas for each case.
- Hourly labor cost formula
Hourly Labor Cost = (Total Labor Cost)/(Total Hours Worked)
- Daily labor cost formula
Daily Labor Cost = (Total Labor Cost)/(Total Workdays in a Given Period)
Understanding these daily and hourly costs can lay the foundation for efficient labor cost management.
Industry-specific labor cost calculations
Different industries have unique considerations when calculating labor costs. Let’s explore two major sectors: construction and manufacturing.
Calculating labor cost in construction
In the construction industry, labor costs are a significant portion of project expenses (high labor cost percentage). Accurate calculation is crucial for bidding, budgeting, and project profitability. Here’s how to approach it.
Here is a list of direct labor costs in the construction industry:
- Wages, salaries, and overtime pay for carpenters, electricians, plumbers, masons, laborers, and equipment operators
- Employers pay performance-based bonuses or incentives to workers for meeting project milestones or exceeding productivity targets
- Payroll Taxes
- Workers’ compensation insurance
- Project-specific equipment unique to a particular project
Here is a list of indirect labor costs in the construction industry:
- Salaries of supervisors and project managers
- Salaries for office staff, accountants, HR personnel, and other administrative employees who support the construction operations
- Health insurance, retirement plan contributions, paid time off, and other employee benefits for direct and indirect labor employees
- Training, recruitment, travel, and per diem costs
- General safety equipment like hard hats, safety glasses, gloves, and high-visibility vests that aren’t tied to any specific project
Labor cost calculation in manufacturing
Calculating costs in the manufacturing industry is just as crucial and includes just as many factors as in other industries. You must consider not only the employees running the machines but also the employees tasked with managing the employees and maintaining those machines and their software.
Here is a list of direct labor costs in manufacturing:
- Wages, salaries, and overtime pay for assembly line workers, machine operators, and production technicians
- Performance-based bonuses or incentives tied to production targets, quality metrics, or other performance indicators
- Employer-paid taxes on employee wages, including Social Security, Medicare, and federal and state unemployment insurance
- Workers’ compensation insurance
- Subcontractor costs
- Piece-rate pay
Here is a list of indirect labor costs in manufacturing:
- Salaries of supervisors, managers, engineers, technicians, and other technical experts who design, maintain, and troubleshoot manufacturing processes and equipment
- Health insurance, retirement plan contributions, paid time off, and other employee benefits for direct and indirect labor employees
- Salaries and wages for employees in inventory and supply chain management
- Salaries of quality control personnel and maintenance staff
- Recruitment and training costs
- General safety equipment
Tools and techniques to calculate labor costs
Gone are the days of relying solely on spreadsheets and manual calculations. Today, businesses have access to a wide range of sophisticated tools and techniques to streamline labor cost analysis. It’s similar to how the best NPS survey tools can automate the collection and analysis of customer sentiment.
Manual calculation vs. automated systems
While manual calculation using spreadsheets can be effective for smaller businesses, it can become cumbersome and error-prone as your workforce grows. Automated systems offer several advantages:
- Accuracy. Automated systems minimize the risk of human error in calculations.
- Efficiency. Automated systems streamline data collection and analysis, saving time and resources.
- Real-time insights. Many automated systems provide real-time labor cost data, allowing you to make informed decisions to reduce labor costs.
- Scalability. Automated systems can easily adapt to your business’ growth.
Recommended software for labor cost analysis
Several software solutions cater to labor cost analysis and management. Here are a few popular options:
- Hubstaff. This time tracking, workforce analytics, and project management software provides detailed insights into labor or employee costs, productivity, and project progress. GPS and geofencing features make it easier for distributed teams to automate clock-ins and clock-outs to reduce overtime costs. It’s also an ideal tool to calculate labor costs, gross pay, labor cost percentages, fixed labor costs, and more.
- QuickBooks Time. Formerly known as TSheets, this time tracking and scheduling software offers time tracking, robust reporting features, and GPS and geofencing for labor cost analysis.
- Gusto. This payroll and HR platform simplifies payroll processing and provides tools for tracking labor costs and employee benefits. It also integrates with time tracking tools for more accurate payments.
- Paychex Flex. This comprehensive HR and payroll solution includes features for labor cost tracking, budgeting, and compliance.
Managing labor costs in a small business
Small businesses often face unique challenges when it comes to labor cost management due to limited resources and a smaller workforce. However, with the right strategies, you can reduce labor costs, improve labor cost percentages, and maintain a healthy bottom line.
Strategies to optimize labor spending
The following are ways to get the most value for your money when it comes to labor spending:
- Efficient scheduling. Optimize your work schedules to match demand and avoid understaffing (and the ensuing overtime costs) or overstaffing during slow periods.
- Online training. Invest in an LMS system to train employees online. These systems help by increasing flexibility and also reduce the need for additional labor and training costs.
- Outsourcing. Consider outsourcing non-core tasks to specialized service providers. Outsourcing offers a number of benefits, but, most importantly, it helps you save on labor costs.
- Technology adoption. Embrace technology solutions like Hubstaff and other time tracking software and project management tools to monitor labor usage and identify inefficiencies.
- Regular review. Regularly review your labor costs and compare them to industry benchmarks to identify areas for improvement.
Case studies of successful labor cost management
Let’s look at some examples of how businesses have effectively managed their labor costs:
- Case Study 1: Everbuild (construction company)
The construction company Everbuild found that Hubstaff helped them manage and reduce labor costs. In fact, they reported savings of one to two hours of work every two weeks.
Previously, Everbuild tracked time with mental lists and timesheets, which were inaccurate and time-consuming. Hubstaff allowed Everbuild to see labor costs in real-time, which then allowed them to identify profitable jobs and avoid unprofitable ones.
- Case Study 2: Love Furniture (an online furniture store)
The online furniture store Love Furniture wanted to cut overhead costs by hiring remote workers. However, managing a remote team presented a challenge and relied entirely on trust. They opted for time tracking software, and after going through several options that didn’t work out, they chose Hubstaff.
Love Furniture found that Hubstaff’s time tracking and monitoring tools helped them to ensure that their remote workers were productive. Overall, the decision to use time tracking software was a successful strategy for reducing actual labor costs in e-commerce.
Common mistakes and how to avoid them
Even seasoned business owners can fall prey to common mistakes in labor cost management. Let’s explore two prevalent pitfalls and how to steer clear of them.
Overlooking hidden costs
Beyond wages and salaries, various hidden costs can significantly impact your labor budget. For example, it’s common for small businesses to overlook annual costs like recruitment, training, turnover, and absenteeism.
To avoid these labor expenses, invest in employee retention programs, provide adequate training, and create a positive work environment that makes workers want to come in.
Failing to account for overtime and benefits
Overtime pay and employee benefits can lead to significantly higher labor costs if not properly managed. It’s important to track the number of hours that go into overtime effectively and factor them into your budget. When calculating total labor costs, include the cost of benefits such as health insurance, retirement contributions, and paid time off.
Future trends in labor cost management
The landscape of labor cost management is constantly evolving. Let’s look at some key trends shaping the future.
Impact of technology on labor costing
Technological advancements are revolutionizing how we calculate labor cost. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being used to analyze labor data, predict future costs, and also optimize workforce scheduling.
Cloud-based HR and payroll systems streamline processes and provide real-time insights to lower labor costs.
Preparing for changes in labor regulations
Labor laws and regulations are subject to change and can directly impact your labor costs.
Stay informed about new legislation, minimum wage increases, and other regulatory changes that could affect your business. It’s also important to partner with HR professionals or legal advisors to ensure compliance and avoid costly penalties.
By understanding the evolving landscape of labor cost management and embracing technological advancements, you can then position your business for success in the ever-changing world of work.
Most popular
How to Calculate a Raise: Practical Guide for Employers
By 2030, the US alone will lose $430 billion annually due to low talent retention — and a lot of this turnover stems from low pa...
How to Survive and Thrive in an 80-Hour Work Week
It’s hard to believe that only a century ago, the 80-hour work week was the norm in the United States. Then, in 1926, the Ford M...
Mastering Workforce Scheduling: Techniques and Tools for Success
Imagine a workday where scheduling your workforce effectively ensures that every shift is perfectly aligned with your business nee...
Top Time Trackers for Virtual Assistants: Enhance Efficiency and Accountability
Virtual assistants (VAs) have a lot of responsibilities — and so do the people who hire them. With so much to keep track of, a t...




